In the period 2011-2015 published more than 100 publications, research results are protected by more than 15 patents, recieved 1 doctoral and 4 candidate degrees.
Developed a unique industrial-demand technology of forming composite coatings on aluminum alloys, titanium, magnesium. The coatings have anti-corrosion, anti-wear and superhydrophobic properties, as well as the effect of self-repair after mechanical damage to the surface. inventions related to formation of composite polymer-containing coatings produced using superdispersed polytetrafluoroethylene on titanium alloys, introduced as a pilot plant at the dockyard Far East Plant "Zvezda" in the framework of the RF Government Resolution 218 (2015).
 The technology allows to restore the protective properties of the resulting coatings on heat-expensive products, were in operation.
Report on the status of the basic sciences in the Russian Federation and of the most important scientific achievements of Russian scientists in 2015
The technology allows to restore the protective properties of the resulting coatings on heat-expensive products, were in operation.
Report on the status of the basic sciences in the Russian Federation and of the most important scientific achievements of Russian scientists in 2015
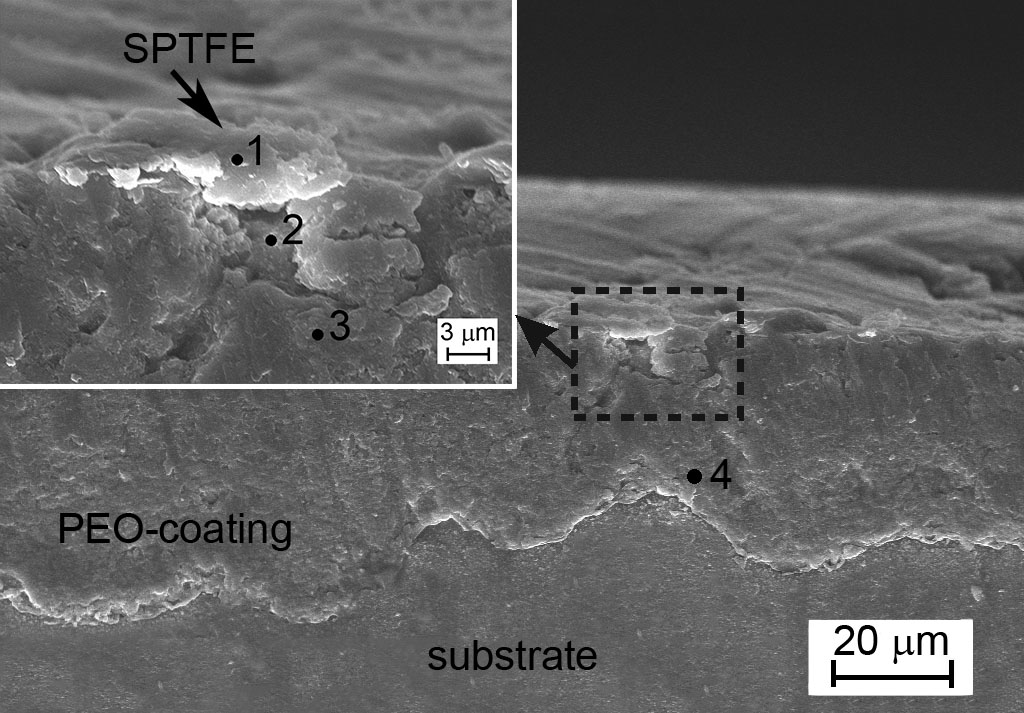
Figure of polymer-composite (SDTFE) protecting coating cross-grinding on the product ships power engineering
Laboratory of unstable surface processes
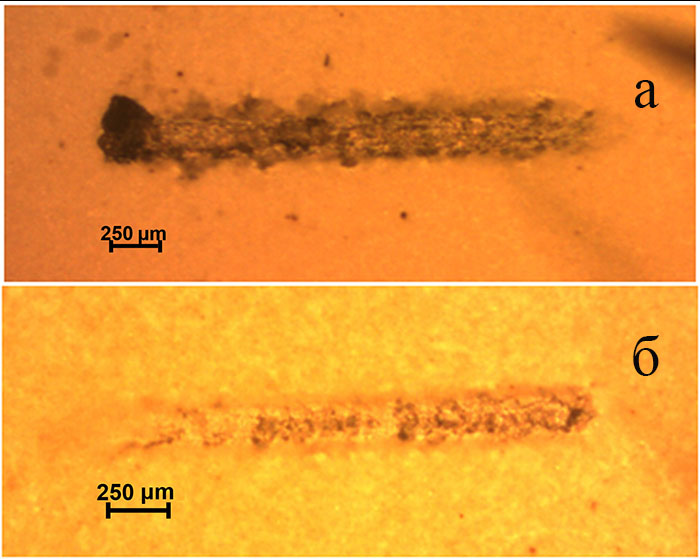 A method of forming selfhealing coatings on magnesium alloys by inhibitor impregnating a base layer obtained using plasma electrolytic oxidation method. Using scaning local electrochemical methods (SVET and SIET) the mechanism and kinetics of self-healing coating process has been studied. PEO-layer treatment in a solution of 8-hydroxyquinoline allows to reduce the current density of corrosion of the sample with composite coating (3,2 μA·cm−2) in corrosive environment in 30 times beside the image with the base PEO-layer (100 μA·cm−2) and thus to prevent intensive destruction of the magnesium alloy due to formation of mechanical damages. Corros Sci 102 (2016) 348–354.
A method of forming selfhealing coatings on magnesium alloys by inhibitor impregnating a base layer obtained using plasma electrolytic oxidation method. Using scaning local electrochemical methods (SVET and SIET) the mechanism and kinetics of self-healing coating process has been studied. PEO-layer treatment in a solution of 8-hydroxyquinoline allows to reduce the current density of corrosion of the sample with composite coating (3,2 μA·cm−2) in corrosive environment in 30 times beside the image with the base PEO-layer (100 μA·cm−2) and thus to prevent intensive destruction of the magnesium alloy due to formation of mechanical damages. Corros Sci 102 (2016) 348–354.
The photography of the locations of mechanical destruction on base PEO coating (a) and composition ingibitor-containig coating after holding the sample in 0.05 M NaCl for 24 hours (b)
Methods for forming on the low-carbon steel, alloys, titanium and magnesium composite superhydrophobic coatings developed. PEO-layers as matrix with the self-organization dispersed silicii dioxydum colloidale nanoparticles using in these methods. Composite coatings have pronounced superhydrophobic properties demonstrating the wetting angle of more than 160º and rolling angle of less than 10º. The anti-corrosion effect of such coatings is provided by electrically insulating oxide and super hydrophobic layers which are resistant to aggressive chlorine-containing medium. Multimodal extended surface of nanocomposite coatings contributes to the realization of a heterogeneous mode of wetting, whereby, real area of contact surface with aggressive media is less than 3%. Corros. Sci. 2012. 55. P. 238–245.
The technologies of forming of protective composite coating has been developed and introduced at "FES "Zvezda". Scientific research is carried out in conjunction with Federal State Unitary Enterprise All-Russian Scientific Research Institute of Aviation Materials (State Research Center of The Russian Federation, Moscow), Russian academy of sciences A.N. Frumkin Institute of Physical chemistry and Electrochemistry RAS (IPCE RAS, Moscow), Institute of metallurgy and materials Baykova RAS (Moscow), Institute of Strength Physics and Materials Science SB RAS (ISPMS SB RAS, Tomsk),
The Institute of High Temperature Electrochemistry of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences (Yekaterinburg), Far Eastern Federal University (FEFU, Vladivostok), Department of Engineering materials, University of Sheffield, UK.
Laboratory of composite coatings for biomedical applications
A method of forming a calcium phosphate bioactive coating by plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO) method on the medical VT6 titanium alloy have been developed. The evaluation of osteo-generating properties of coating for diaphyseal femur of laboratory rats have been done. It was found that the coating obtained by PEO, has a positive effect on the osteosynthesis in the treatment 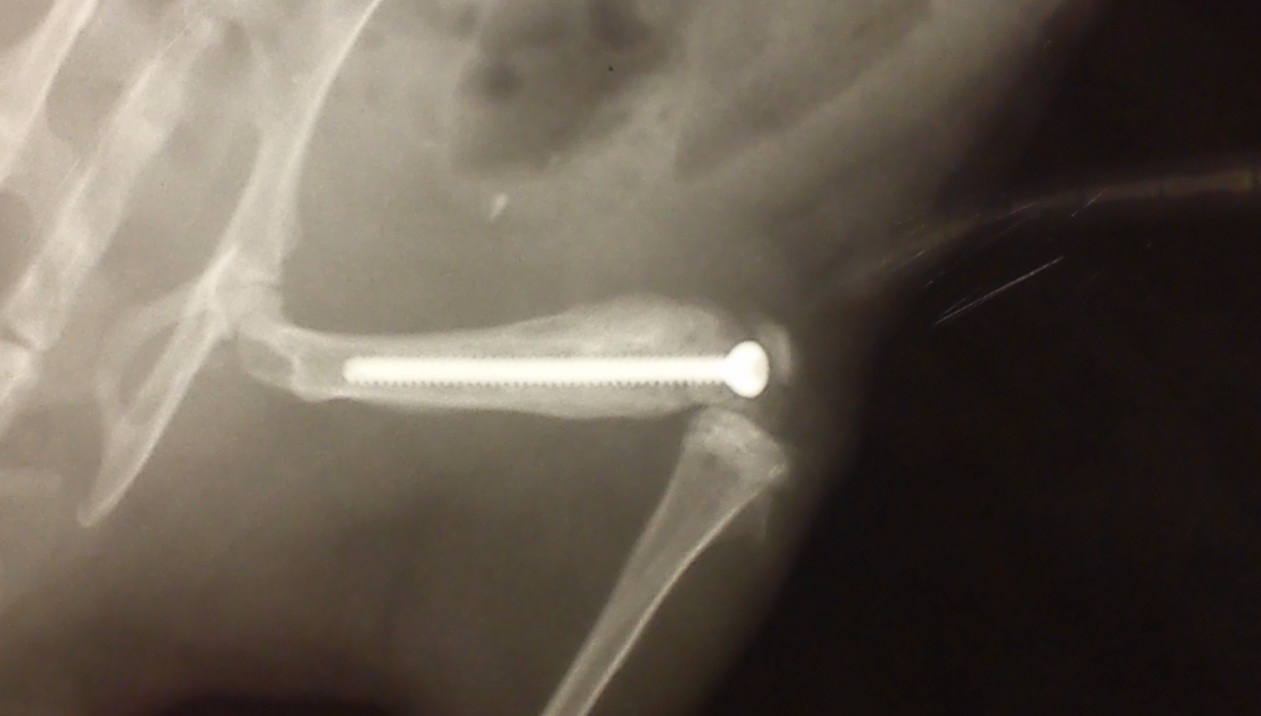 of diaphyseal femur. The hydroxyapatite, which is in the composition of the bioactive coatings acts as an initiator in the growth process of bone formation, drastically reducing the recovery period. Corros Rev 34 (2016) 65–83.
of diaphyseal femur. The hydroxyapatite, which is in the composition of the bioactive coatings acts as an initiator in the growth process of bone formation, drastically reducing the recovery period. Corros Rev 34 (2016) 65–83.
X-ray pattern of the fracture with installed titanium implant with calcium phosphate PEO-coating within 42 days after surgery: pronounced callus, the fracture line is not visible
It was found that the TiNi surface layers obtained by PEO method significantly reduce the diffusion of nickel from the material and thus protects the human body from the harmful effects of this metal. Herewith the PEO coating does not block or reduce the memory effect NiTi. The coatings are promising for practical implant surgery by reason of maintaining substantially high thermal stability and adhesive properties during thermal cycling over a wide temperature range. Prot Met Phys Chem Surf 51 (2015) 127–130.
Electrolytic systems of complex composition, containing SiO2, ZrO2, TiN nanopowders were developed. These systems were used for PEO of MA8 Mg-alloy for developing of protective nanostructured ceramic like coatings, promising for medical bioresorbable implants. The greatest protection against corrosion action and the best mechanical properties exhibits coatings, formed in the electrolyte, containing ZrO2nanoparticles. J nanomaterials (2015) 154298.
A method (electrolytes, modes) of electrophoretic deposition of ultrafine polytetrafluoroethylene on the PEO-layer surface was developed. The essence of the method is to create a reliable protective composite coatings on magnesium alloys that expand the area of practical use of the treated material. It is shown that the polymer-composite coating on Mg-alloy increases anticorrosion characteristics in 3 orders of magnitude and reduce surface deterioration in 2 orders compared to the base-coated PEO. Surf Coat Tech 283 (2015) 347–352.
Group of chemical power sources
It is found that the transition metals (Zr, Mo, Hf) ions doping of nanostructured titanium dioxide present in anatase crystallographic modification is an effective method for producing the promising anode material for a Li-ion battery. Through galvanostatic cycling was shown that introducing zirconium, hafnium and molybdenum ions into the crystalline lattice of TiO2 leads to a substantial increase in specific capacity of the material (from 65 to 150 mAh/g). The reversibility of the electrochemical process is due to: a) the distortion of the parameters of the unit cell, facilitating the diffusion of Li+ cations during intercalation / deintercalation; b) charge redistribution in the lattice, determining the increase in electrical conductivity of TiO2. Scripta Mater. 107 (2015) 136–139.
The electrochemical properties of nonstoichiometric oxyfluoride MoO2.8F0.2, with the lattice parameters close to the layered orthorhombic MoO3, synthesized by solid-phase method were reported. Partial substitution of the O2- anions for F- snions enhances the cycle performance of material as a cathode for Li-ion battery due to shielding the electrostatic interaction between the Li+ ions and MoO6 octahedron layers. By the galvanostatic discharge/charge cycling it was observed that reversible capacity for MoO2.8F0.2 (165 mAh/g) is higher than for commercial MoO3 (120 mAh/g). Conductivity of material after the F/O atomic substitution leading to charge redistribution in the crystal lattice is increased by three orders of magnitude: 4.4x10–9 S/cm (for molybdenum oxide) to 1.8x10–6 S/cm (for oxyfluoride). Mater Lett 160 (2015) 175–178.
Two-phase Al(OH)3–PbSnF4 composites (Al(OH)3 concentration – 5 wt.%, 15 wt.%, and 30 wt.% 5, 15 и 30 мас.%) has been synthesized by high-energy ball-milling method. PbSnF4-based systems show high initial lithiation capacities of 800–1100 mAh/g. It was observed that reversible capacity for Al(OH)3–PbSnF4 (aluminum hydroxide – 15 wt.%) after 10-fold cycling is higher (120 mAh/g) than ones for pure PbSnF4 (20 mAh/g). It has been shown that the deviation from 15 wt.% concentration of Al(OH)3 decreases a cycling stability of the lead fluorostannate(II). The reversibility of the electrochemical process associated with minimization of volume changes during lithiation–delithiation due to the damper properties of aluminum hydroxide matrix. J Energ Chem 24 (2015) 346–352.
Solid solutions in binary systems tetrafluoro stannate–metal-oxide (SnO, PbO, including nano CeO2, SnO2, Al2O3), solid solutions in the system K(1–x)LixSn2F5 (0 < x < 7.5) has been synthesized by high-energy ball-milling method. Correlation between ion mobility, phase transitions, the type of introduced cation and ionic conductivity in these systems has been investigated. Conductivity values reaches ~10–2 S/cm at ~470 K. It was demonstrated that conductivity at ambient temperature of K0.975Li0.025Sn2F5 and K0.95Li0.05Sn2F5 solid solutions are higher than for pure KSn2F5. Thermal and electrical properties in the K(1–x)LixSn2F5 (0 < x < 7.5); system has been investigated; evaluate the effect of substitution of lithium cations for potassium cations in the resulting compounds on the activation energy of charge transfer and structure was evaluated. The prospects of using PbSnF4–SnO2 as cathode materials for lithium chemical power sources was noted. Russ J Gen Chem 85 (2015) 653–658, Solid State P 213 (2014) 200–203.
It was demonstrated the prospects of an original method of pulsed high-voltage discharge in synthesis of nanostructured transition metal compounds as anodes for Li-ion battery. In particular, nanostructured TiO2(anatase)–TiOF2, FeOF–FeF3, MoO3, etc. was synthesized and investigated as Li-ion battery electrodes. J. Alloys Compd 621 (2015) 364–370.
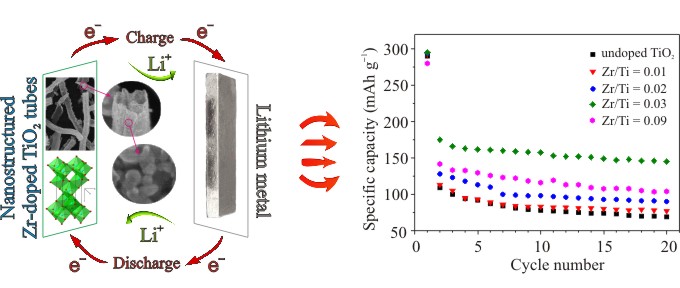
Schematic illustration of half-cell with lithium counter electrode and working electrode consisting of Zr-doped anatase titania. The relationship between reversible capacity and Zr-dopant concentration.
Laboratory of Electrochemical Processes
The features of formation the polymer / nanoparticle Pt, Au composites using one-step electropolymerization (EP) method studied. The kinetics of the process was studied. It was found that the rate of formation and conductivity of polyacrylamide films are increase in the presence of chitosan supplements. The cycling in the range of -1.0 ÷ -1.3 V allows to obtain sufficient thickness of coating with a slight decrease of the current density. It was obtain by impedance spectroscopy method that a maximum isolation effect exhibit the polyacrylamide coatings linked by N,N’- metilen-bis-akrilamid. With increasing concentration H2PtCl6·6H2O from 2 up to 8 mmol/l the platinum content in the film increases from 2.7 at. % to 25 at. %. Using electrooxidation of С2Н5ОН and Н2О2 reduction processes as exemplary on modified electrodes was demonstrated that polymer composites with inclusion of Pt and Au exhibit electrocatalytic properties.
It has been found previously unknown phenomenon, indicating that the zinc metal has a catalytic effect on the process of initiating polymerization of acrylamide formation and coatings in currentless mode. The kinetic and mechanism of zinc initiate polymerization (autoelectropolymerization AEP) was investigated. It has been found that the other metals with equilibrium electrochemical potential sufficient to discharge the zinc complex of acrylamide in the one-dimensional solution can act as an initiator. The optimal conditions for AEP identified. It allowed to form the qualitative polimetilacrylamide coverage with minimal economic costs.
The possibility of the formation of the electrode material for electrochemical capacitors based on polyacrylamide gel (PG) produced by EA, followed by the introduction into it of silver nanoparticles was shown. The asymmetric structure of matrix asymmetric structure of the matrix layer thickness of composite PG / Ag established. Silver content therein varies from 70.9 to 100%. The amount of silver in the composites without chitosan is 10-15 times higher than that with the addition of chitosan. The chitosan AgO nanoparticles impregnated in the polymer matrix, have spherical shape with a radius of 120-145 Ǻ, exhibit high stability and do not change color over time. The polymer / silver composite exhibits selectivity towards Н2О2. It is shown that PG with impregnated into the matrix crystal silver can be an alternative to carbon electrode materials for capacitors. When the concentration of silver nitrate solution doubles in the film, the mass of reduced Ag0 in the film increases in equal proportions, while the capacitance is increased about 1.5 times.
The methods of modifying the surface of the ion-exchange membranes using pyridinium salts, sodium alginate or chitosan, crosslinked with glutaraldehyde or epichlorohydrin were designed with the aim to create electrodialysis membranes, which selectively permeable for cations or anions with different charge magnitude. A comparative analysis of the efficiency of MK-40 sulfonated membrane using for electrodialysis separation of similarly charged ions (cations Na+, Mg2+, Ca2+) was held. The surface of above mentoned membrane modified by various methods. It is shown that that the most promising modification method is the electrodeposition of chitosan layer directly in the electrodialysis device (in terms of improved selective permeability of the membrane to the singly charged ions). It was found that the most durable and long-lived film obtained by cross-linking of chitosan with an epichlorohydrin.
to the beginning
 The technology allows to restore the protective properties of the resulting coatings on heat-expensive products, were in operation.
The technology allows to restore the protective properties of the resulting coatings on heat-expensive products, were in operation.
 of diaphyseal femur. The hydroxyapatite, which is in the composition of the bioactive coatings acts as an initiator in the growth process of bone formation, drastically reducing the recovery period. Corros Rev 34 (2016) 65–83.
of diaphyseal femur. The hydroxyapatite, which is in the composition of the bioactive coatings acts as an initiator in the growth process of bone formation, drastically reducing the recovery period. Corros Rev 34 (2016) 65–83.
